This is a guest post by exhibit curator Sabrina Oliveros
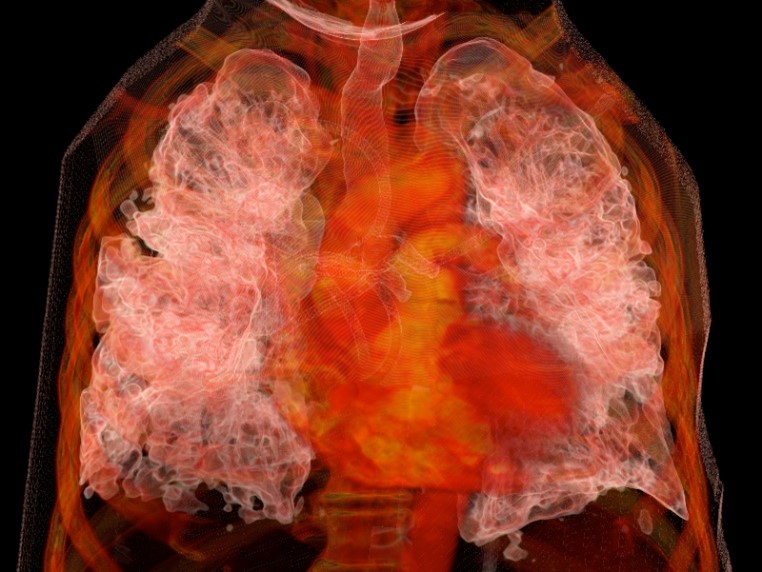
Original engravings from the 17th through the 19th centuries. Facsimiles of masterworks by Andreas Vesalius and Leonardo da Vinci. Images produced through technologies developed at UCSF – including a three-dimensional rendering of a patient’s lungs with COVID-19.
See all these groundbreaking images from the history of medicine, and many more works of science and art, at an exhibit opening in May 2022 at the UCSF Library.
Entitled Seeing the Self Anew: How Art and Science Intersect, this exhibit uses anatomical atlases, medical artifacts, and other materials from UCSF Archives & Special Collections to explore some ways that artists and scientists have informed each other’s work when examining a common subject: the human body.

Collaborations and inspirations
On one level, the relationship between artists and scientists is collaborative. As scientists uncover new knowledge about the body, artists put this information into visual form, recording and disseminating it.
Exhibits in the library’s main lobby feature such collaborations, which, at the times of their publications, counted as the most accurate and attractive anatomical atlases the world had seen. These include books like De humanis corporis fabrica (1543 facsimile) by Andreas Vesalius, which set new directions for the art and science of anatomy; Osteographia (1733) by William Cheselden, which showed the bones in life-like size and detail; and the pioneering manuals on obstetrics by William Hunter (1774) and William Smellie (1793 edition).
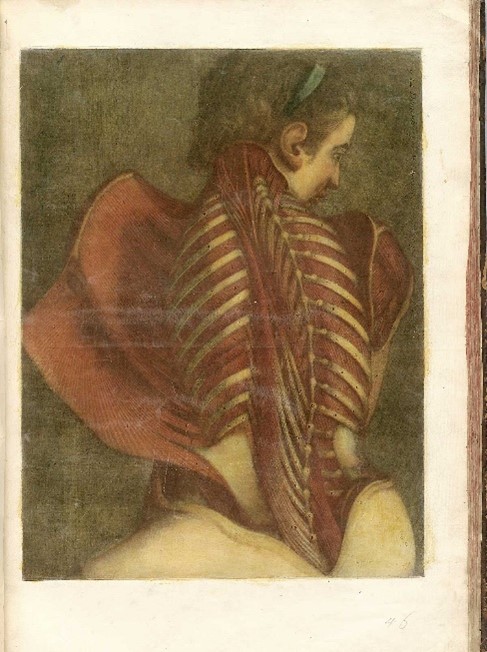
Other displays also show what is created when artists engage with the science of depicting the human body – best exemplified in the works of Albrecht Dürer and Leonard da Vinci.
More featured illustrations – like “The Flayed Angel” (1746) by Jacques Fabian Gautier d’Agoty, and fantastical skeletons by Jacques Gamelin (1779) – arguably have less instructional value for medical students. Still, they suggest how anatomical studies inspired artists to produce compelling images all their own.
The rare books and artifacts on this floor are supplemented by images from the National Library of Medicine.
Inventions and new dimensions
Art and science also intersect in engineering, where drawings guide the design of instruments. From microscopes and stereoscopes to x-rays and MRI technology, these instruments facilitate further studies, procedures, and treatments that produce even newer images of the body.
Exhibits on the library’s fifth floor offer a glimpse into such designs. These include conceptual sketches and models envisioned by early 20th-century UCSF professionals like Verne T. Inman, Howard C. Naffziger, and Saxton T. Pope.
The fifth-floor displays are highlighted by selections from Images, the official publication of the UCSF Department of Radiology and Medical Imaging, dating from 2012 to 2021. With detail and depth that perhaps even the most accomplished early modern artist-anatomists could not have imagined, these illustrations show how far scientists have come – and how much farther they can go – in enabling us to see, and understand, our bodies and our selves anew.
Seeing the Self Anew will be on display on two floors (third and fifth) of the UCSF Library at Parnassus through Spring 2023. UCSF Library is currently open to UCSF faculty, staff, and students via ID badge access Monday–Friday from 7:30am–6pm. Changes to in-person library access will be shared through library website as UCSF policies and guidelines are updated in the coming months.