The UCSF Library Archives and Special Collections is pleased to announce the digitization of the Selma H. Fraiberg papers and Helen Fahl Gofman papers. The digitization of the collections is part of our current grant project, Pioneering Child Studies: Digitizing and Providing Access to Collection of Women Physicians who Spearheaded Behavioral and Developmental Pediatrics, supported by the National Historical Publications and Records Commission (NHPRC). The grant supports the creation of digital collections on Calisphere containing materials from five collections held at UCSF. These collections document the life and work of five women physicians and social workers. The finding aids for theses collections are available publicly on the Online Archive of California.
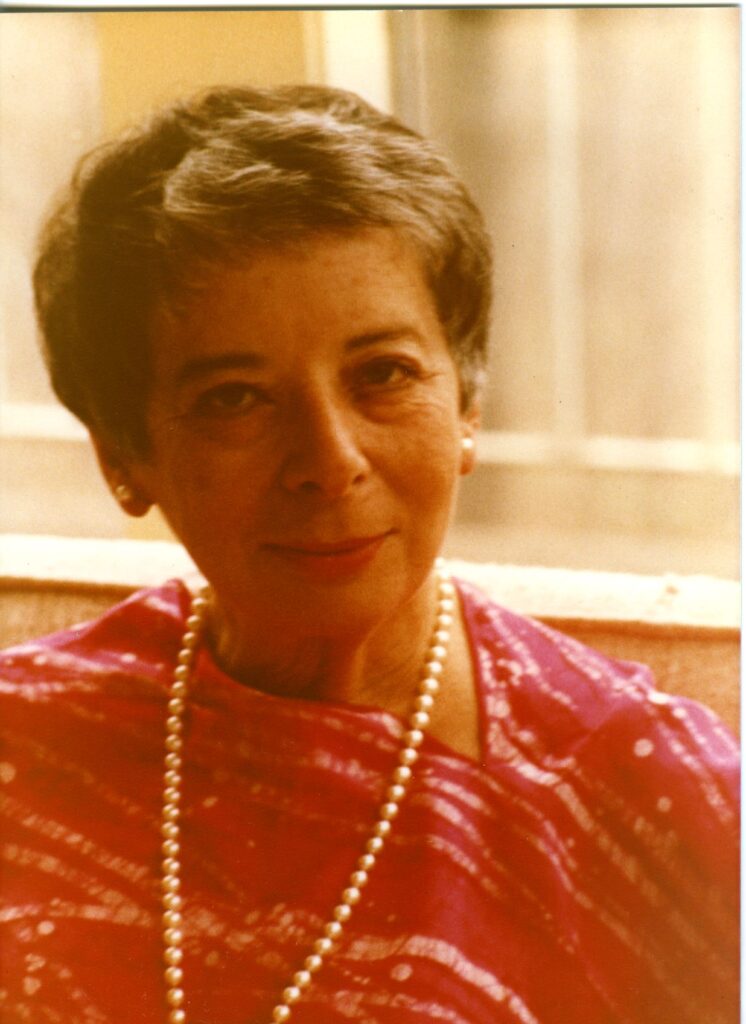
Selma H. Fraiberg
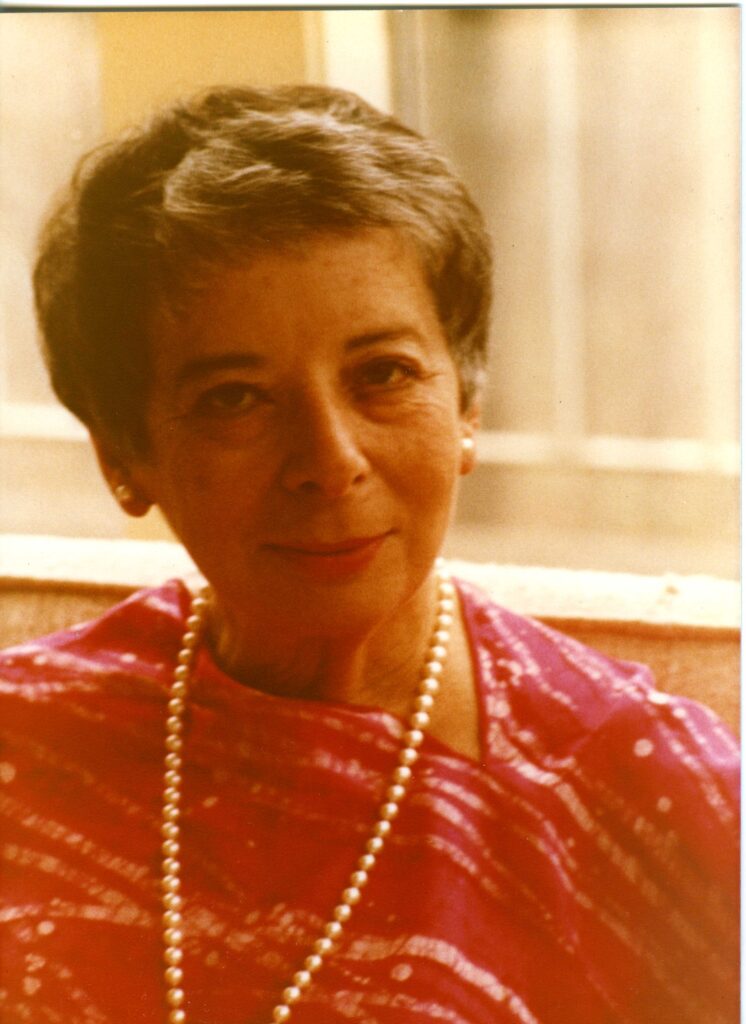

Selma Fraiberg was born in Detroit, Michigan, where she received her education, graduating from Wayne State University with a B.A. in 1940. In 1945, she received her M.S.W. from the same institution and later completed her psychoanalytic training at the Detroit Psychoanalytic Institute. She became lecturer in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Michigan Medical School at Ann Arbor. By 1968 she was professor of child psychoanalysis, becoming professor emeritus on her retirement in 1979. She was also professor of social casework at Tulane University, 1958-61, and lecturer and supervising child analyst at the Baltimore Psychoanalytic Institute, 1961-63. In 1967-69 Mrs. Fraiberg was lecturer and supervisor of the Child Psychoanalytic Program, of the Michigan Psychoanalytic Institute. In 1979, she taught at the University of California, San Francisco, as professor of child psychoanalysis, a position she held at her death in 1981. Mrs. Fraiberg was the author of four major books, including The Magic Years (1959) and Insights from the Blind (1977), both written with her husband, and Every Child’s Birthright: In Defense of Mothering (1977). The digital collection includes correspondence, teaching files, typescripts, manuscript drafts, project materials, meeting notes, lecture notes, articles, and grants. Mrs. Fraiberg wrote several articles regarding child development, but also wrote about parental development including one called, On Being the Parent of a Two Tear Old. Fraiberg wrote, “Knowledge of one’s own Imperfections as a parent soften the criticism of childhood. Many parents now discover a new and deeper understanding of themselves and their relationships to their own parents, and a compassion for their own parents which comes out of identification with the parental role.”
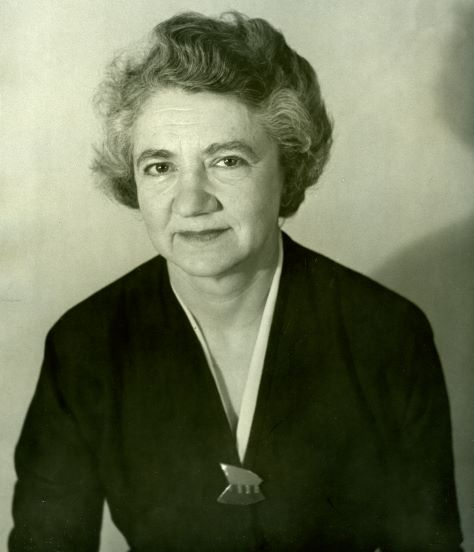
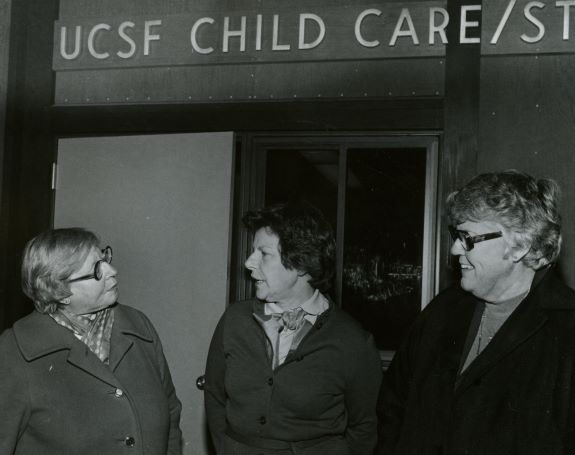
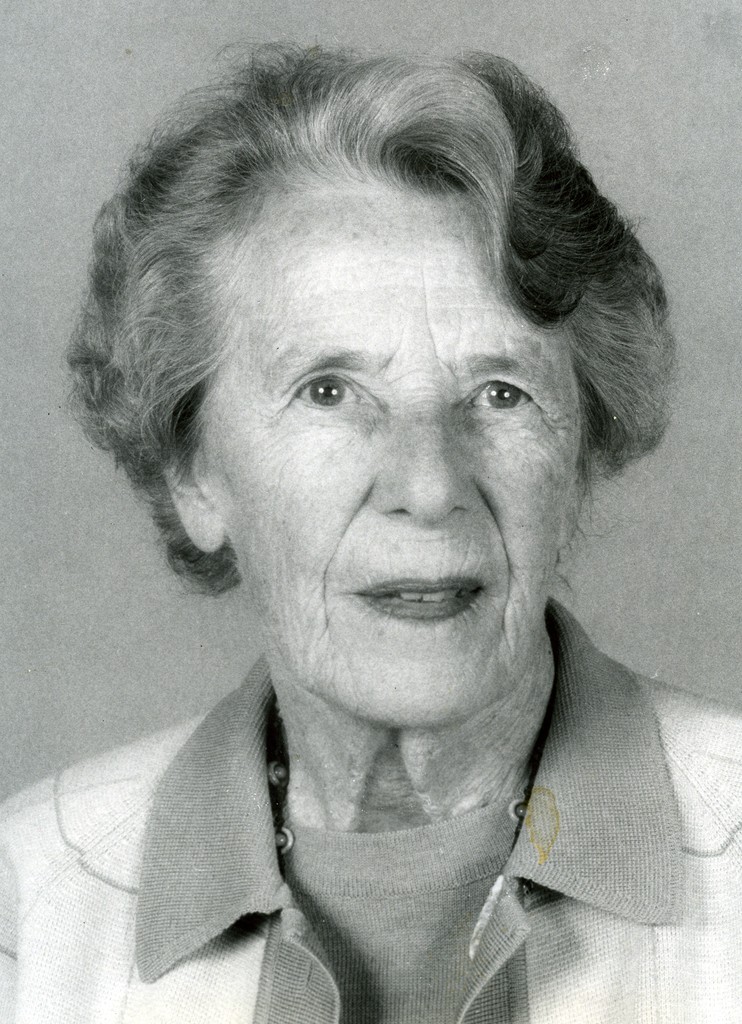
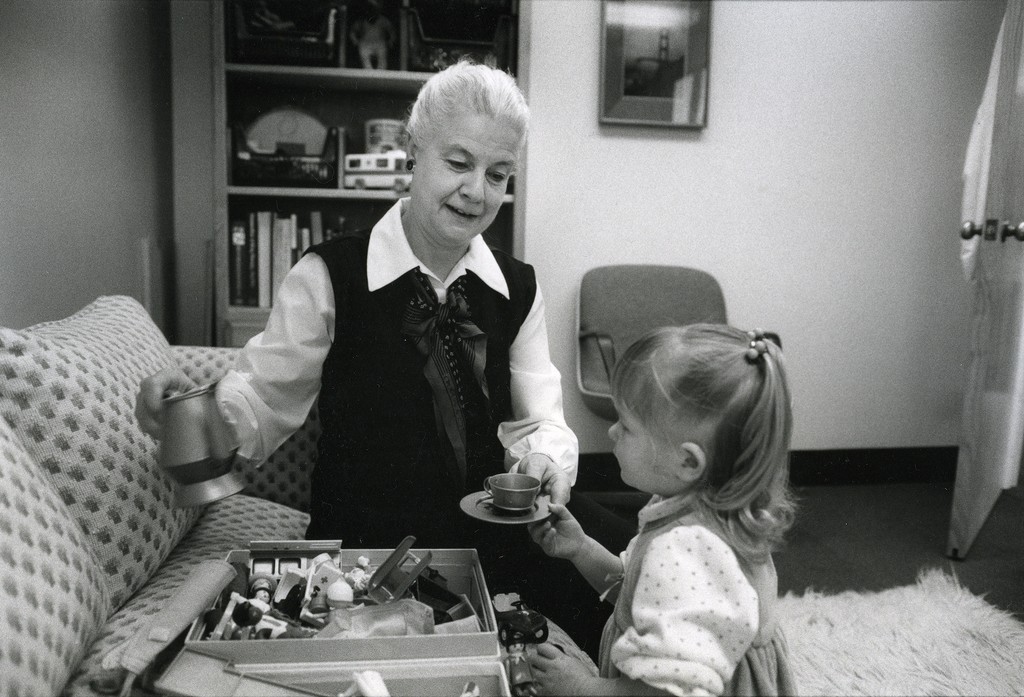
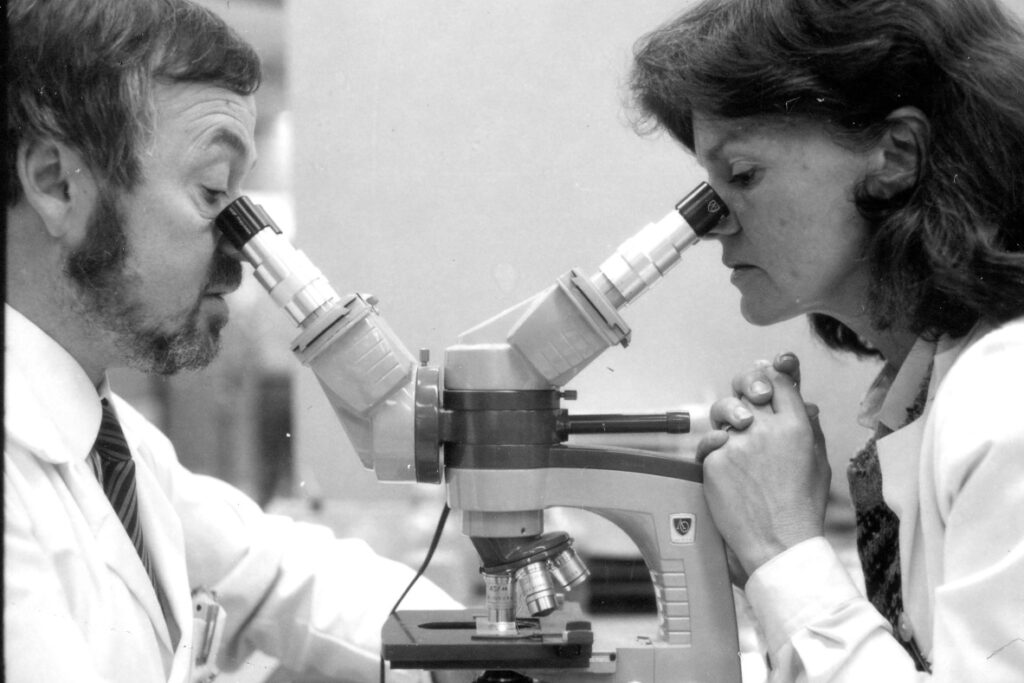
Helen Fahl Gofman
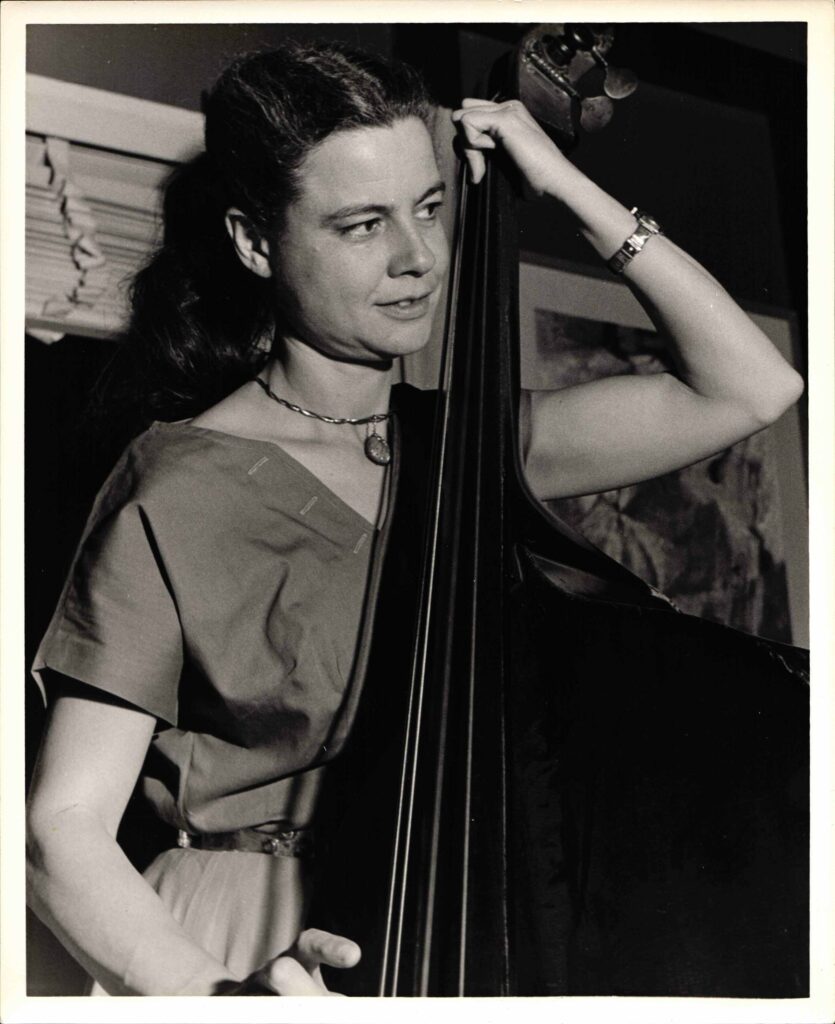

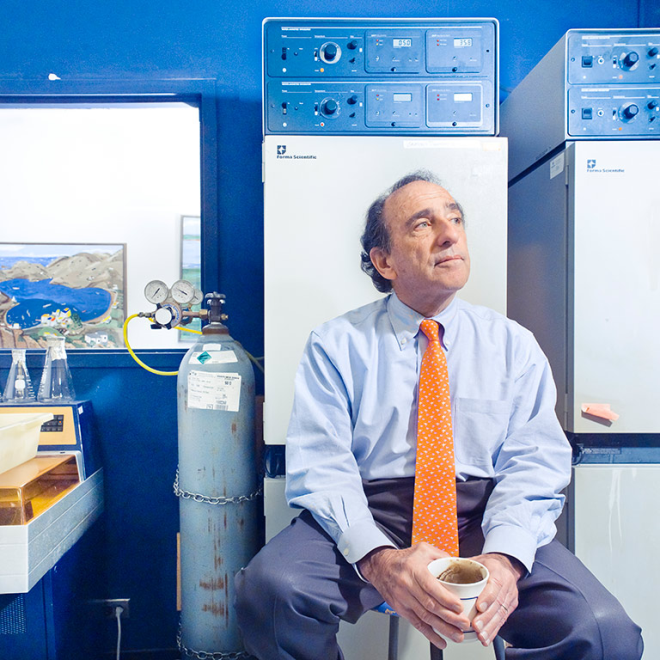
Dr. Helen F. Gofman was involved with teaching, patient care, and research at the University of California for 42 years. Gofman was a national leader in the field of behavioral pediatrics. She completed both her medical degree and a residency in pediatrics at UCSF in 1947. Gofman next was involved with the Child Study Unit (CSU), within the UCSF Pediatrics Department, from the time it was founded in 1948 until her retirement in 1984. She served as director of the CSU from 1961-1973 and co-director from 1973-1983. Upon her retirement in 1984, Gofman was awarded professor emeritus. The digital collection contains documents of the life and work of Dr. Gofman. Materials include writings, lectures, correspondence, publications, research materials, diagnostic tools and tests, photographs, and biographical materials. Towards the end of her career, Dr. Gofman wrote her Final Note, a note regarding the positive and negative changes she has seen in her field of behavioral pediatrics, she wrote,” I have seen a tremendous change in the teaching and acceptance of biopsychosocial issues as part of pediatric practice…In the field of behavioral pediatrics, there were no textbooks, manuals, or syllabi available; in fact, the term behavioral pediatrics was, as yet, unknown. And yet, I think many pediatric housestaff were hungry for training in this area…It is unfortunate that lack of funds in medical schools, state and federal budgets threaten to stunt it’s growth at this time. I see this as a critical time for behavioral pediatrics and for pediatrics itself.”