Guest post by Noel Salmeron, 2023 Senior Data Science Fellow for the Industry Documents Library and Data Science Initiative.
Hi everyone! I had the opportunity of interning for the Industry Documents Library in coordination with the Data Science Initiative as the Senior Data Science Fellow for the Summer of 2023. I am working towards my Bachelor’s degree in Data Science and minoring in Education, and I plan to graduate in May 2024. I feel grateful that I could earn this position with UCSF and work with the fascinating Industry Documents Library as I realize how valuable archives and data are, especially when doing my own research. The Data Science Initiative was extremely helpful in teaching me Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing topics pertinent to the project and valuable for my future in data science.
Project Background
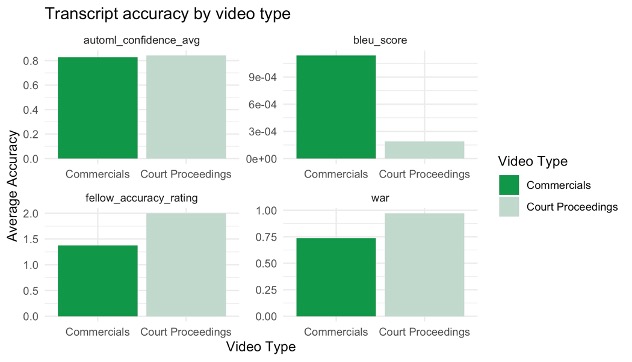
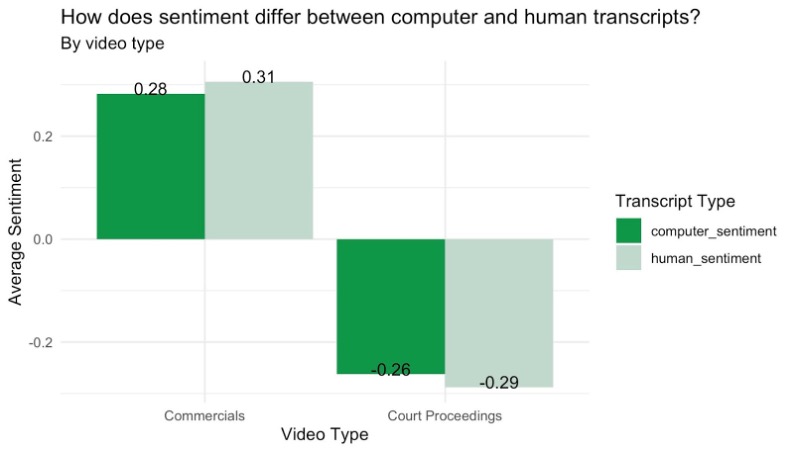
Currently, the Industry Documents Library contains more than 18 million documents relating to public health, as well as thousands of audiovisual materials, such as “recordings of internal focus groups and corporate meetings, depositions of tobacco industry employees, Congressional hearings, and radio and TV cigarette advertisements.” With this project, we wanted to evaluate the transcription accuracy of digital archives and its impact on documentation and the creation of subject words and descriptions for such archives.
Project Team
- Kate Tasker, Industry Documents Library Managing Archivist
- Rebecca Tang, Industry Documents Library Applications Programmer (and Junior Fellows Advisor)
- Geoffrey Boushey, Head of Data Engineering (and Senior Fellow Advisor)
- Rachel Taketa, Industry Documents Library Processing and Reference Archivist
- Melissa Ignacio, Industry Documents Library Program Coordinator
- Noel Salmeron, Senior Data Science Fellow
- Adam Silva, Junior Data Science Fellow
- Bryce Quintos, Junior Data Science Fellow
Project Terminology
Here are a few important terms to note!
- Metadata: a set of data that describes other data (i.e., author, date published, file size, etc.)
- Classification: categorizing objects (or text) into organized groups
- Text cleaning: reducing complex text to simple text for more efficient use in Natural Language Processing
And a few terms were used interchangeably throughout this project!
- Description / Summary
- A condensed version of some text
- Subject / Tag / Keyword / Topic
- A single word that helps to define the text or frequently appears within the text
Project Objectives
Overall, the project had a couple of main objectives. The team wanted to train a Machine Learning model to extract subjects from Industry Documents Library video transcripts and evaluate the accuracy of the machine-generated subjects. We planned to utilize the junior interns’ datasheet they created with subjects and descriptions for over 300 videos to train the model for each tag we chose to analyze.
(The video transcripts were generated beforehand by Google AutoML with the help of Geoffrey Boushey).
Transcript Cleaning
Once the video transcripts were created from Google AutoML, I was able to clean the text using techniques I learned from previous Data Science Initiative workshops. The “Machine Learning NLP Prep” workshop techniques were especially helpful for this portion of the project. I began by setting all 324 transcripts in our dataframe to a lowercase format. This helps simplify text analysis in the long run, especially when avoiding case sensitivity complications. My next step was to remove stop words, which are common and redundant words such as articles, conjunctions, and prepositions. This was possible with the Natural Language Toolkit library for Python, which contains a list of stop words I could add to since I especially noticed ‘p.m.’ and ‘a.m.’ appearing in depositions. I continued by removing everything that isn’t alphabetic using a regular expression (or regex), a sequence of characters corresponding to a pattern to be matched. Any single characters or two character pairs were also removed. Finally, it was essential to stem words to be able to group common words without worrying about suffixes.
ML Model Creation using ID and subject/tag
After text cleaning, we set video IDs as their indices in our running dataframe to efficiently and consistently identify them. Our running dataframe consisted of a row for each of the 324 videos with columns that denoted their ID, subject words, transcript, and a category value of ‘0’ for ‘no’ or ‘1’ for ‘yes’ that corresponded to whether or not the video’s subjects words included the specific tag we were after in each single-tag analysis.
To provide a more concrete example, we will use the “lawsuit” tag, which means each video was denoted with a ‘1’ in the category column if it contained the “lawsuit” tag from the junior interns’ datasheet.
Continuing, we created training and test sets from the dataframe with a 50/50 split. This was followed by a pipeline of several operations in a sequence that included Count Vectorization and Random Forest Classification. Count Vectorization is a method in Natural Language Processing to convert text into numerical values primed for Machine Learning. This way, we can note word frequency in each word for each transcript. Furthermore, Random Forest Classification is a collection of decision trees that make binary decisions based on input and continually “bootstraps” (re-samples) from the training data set to make predictions about whether or not a video contained the “lawsuit” tag.
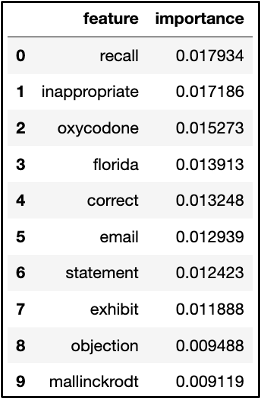
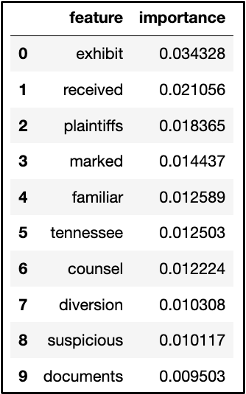
Features for Each Tag
We then gathered feature words and their importance values as to how they supported the model in determining if a video belonged to the “lawsuit” tag. These feature words included “exhibit,” “plaintiffs,” “counsel,” and “documents,” which change every time we run the model. It appears the less common words also slipped through, such as the company name “Mallinckrodt,” which may not appear as important in other transcript datasets relating to lawsuits.
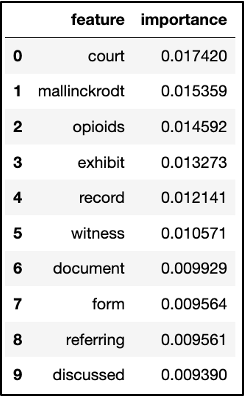
Cross Validation and Match Probability
Moving forward, we used Cross Validation to verify that the model’s performance was not drastically different with different training and test subsets from the running dataframe. Following this process, we were able to create a dataframe that included a column “y_adj” to indicate “Not” for the video not falling under the “lawsuit” tag and an indication of “Match” otherwise. Moreover, we included two columns, “prob_no_match” and “prob_match,” that denote the model’s assessment of the probability that a video doesn’t fit under “lawsuit” or does, respectively.
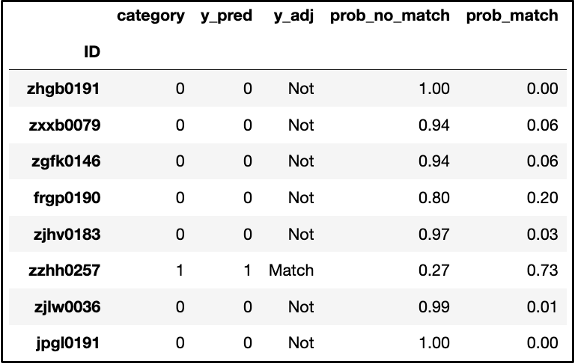
We also ran some code that narrowed down the dataframe to videos where the model incorrectly predicted a video’s match.

This is where we began to run into issues with this dataset since it contained a relatively small amount of videos and, therefore, a low number of videos where the “lawsuit” tag applied. The “lawsuit” tag was filed under only 26 of the 324 videos, a mere 8 percent of the dataset. It was also quite difficult to discern an appropriate threshold for whether or not a video transcript should be marked as a match to a tag because the videos that the model marked incorrectly usually appear to have significantly different probabilities for matching.
This caused our models for tags with counts under 25 or so to result in a non-existent F-score, as well as precision and recall, but a high accuracy which I will explain shortly. Meanwhile, an F-score is critical in providing an overall measure or metric for the performance of a Machine Learning model using its precision and recall.
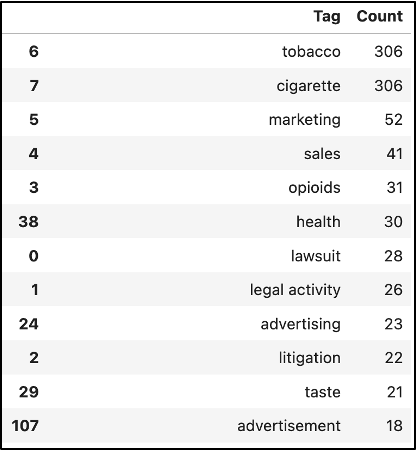
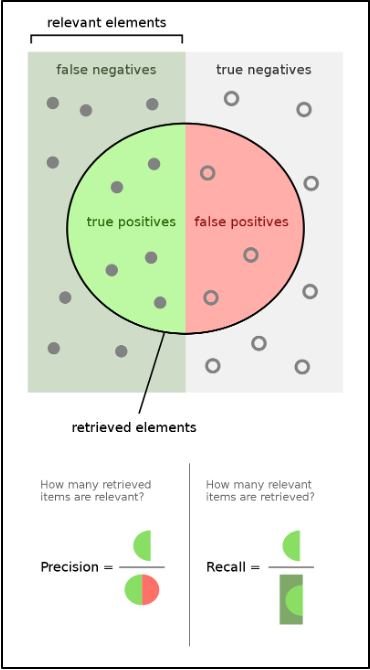
Precision & Recall
Diving into Precision and Recall, Precision can be defined as the proportion of correct positive predictions in the number of predicted positive values, while Recall is the proportion of correct positive predictions in the number of actual positive values.
In this project, the positive values would be video matches for a tag, so in terms of the project, precision is the proportion of correct match predictions out of the predicted matches, and recall is the proportion of correct match predictions out of the actual, true matches. In addition, Accuracy refers to the comprehensive correctness of all positive and negative predictions.
This image may also help visualize the precision/recall relationship:
Thresholds
Another step we took in this project’s analysis was creating precision-recall curves for specified thresholds by the Scikit-learn library that allows for Machine Learning in Python. This way, we could recognize that as the threshold for the probability of a match increases, the precision slowly increases from about 90 percent to 100 percent. In comparison, the recall decreases from 100 percent to 0 percent.
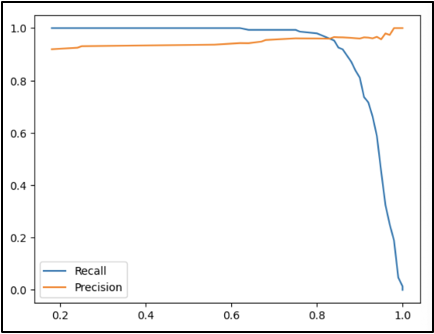
This can be explained by referring back to the definitions of precision and recall! Suppose the threshold for the probability of a match increases and becomes stricter. In that case, precision (the proportion of correct matches out of predicted matches) will only increase as the requirement for a video to be labeled as a match becomes stricter. Regarding the recall (the proportion of correct match predictions out of the actual matches), it becomes clear that since there is more precision, there will be no videos incorrectly marked as matches or any videos correctly marked as matches.
Opportunities for Further Research
There were a few concerns and curiosities that I ended the beginning of this project with since it was simply a pilot, and there is much more to be explored. This includes more text cleaning in subjects/tags and transcripts to make the Natural Language Processing as streamlined as possible. Additionally, it would be crucial to explore this same analysis of subjects/tags for descriptions/summaries that we could not get to. Having a fully-developed human-made datasheet for a larger dataset to explore would also be incredibly useful.
Conclusion
I am pleased to have been a part of this team with UCSF’s Industry Documents Library and Data Science Initiative this summer, as it provided me with extensive real-world experience in data analysis, machine learning, and natural language processing. It truly puts into perspective how much valuable data is out there and all of the fascinating analysis you can conduct.
Prior to this summer, I had worked with various datasets in classes, but I felt inspired by the IDL’s endeavor to enhance its vast collection and make it easier for users to search through documents with supplementary metadata. I can especially appreciate this as I have spent countless hours sifting through documents for research papers in the past. Once the subject and description generations are in full effect, I can only imagine the potential of this data and what it could lead to, as I hope it supports other people’s work.
I also tremendously appreciate the time and effort the junior interns, Adam and Bryce, put into populating their datasheet after watching hundreds of videos. Their work was foundational to getting this project running.
I also want to express my appreciation for Geoffrey and Rebecca throughout this summer for working closely with me, making me feel welcome, and addressing any concerns or questions I had during my fellowship. I am incredibly grateful for this work experience with exceptional communication, collaboration, and kindness.
Thank you to UCSF and everyone on this team for an enjoyable and fascinating fellowship experience!
Addendum: When Should We Apply a Subject Tag to an Uncategorized Document?
By Geoff Boushey, UCSF Library Head of Data Engineering
Overview
Noel described the process for creating a machine learning (ML) model, analyzing the features that go into classifying a document, and applying the model to estimate the probability that a transcript generated from the Tobacco or Opioid collection should be included in a subject tag, such as “marketing,” “legal,” or “health.”
Because most tags in the collection show up in less than 10% of the records in our training and testing set, we shouldn’t expect most tags to apply to most records. As a result, we’re looking for a relatively rare event. If we were only concerned with the overall accuracy or our model, we could achieve 90% effectiveness by never applying a specific tag to a record.
The output from our machine learning model reflects this low probability. By default, our machine learning model would only include a tag if it estimates that the probability of a match exceeds 50%. Because we’re trying to predict a relatively rare event (again, a specific tag would only apply to at most 10% of the records in a collection), it’s unlikely that we’ll have many predictions that exceed this threshold. In fact, when we test our model, we can see that records that clearly (based on human observation) belong to a specific category may have no more than a 30-40% estimated probability of belonging to this category according to the ML model. While this is below the default 50% threshold, it does represent a much higher probability than random chance, (30-40% vs 10%).
We don’t want to erroneously include a tag too often, or it will become clutter. We don’t want to erroneously exclude it too often, or researchers will miss out on relevant record matches. We may want to lower the threshold for determining when to apply a tag to a particular record, but the right threshold isn’t always clear, and can vary depending on the frequency of a tag, the accuracy of our model, and the scenario-dependent benefit or harm of false positives versus false negatives.
The harm of false positives or negatives depends heavily on the research or use scenario. For example, a researcher who wants to retrieve all reasonably likely matches and is not concerned with the inclusion of a few documents that are not related to litigation might want to set the threshold very low, even below 10%. Alternatively, a researcher might simply wish to sample a small number of litigation-related documents with a very high level of accuracy. In this case, a high threshold would be more beneficial.
Precision and Recall curves can help find an optimal threshold that strikes the right balance between false positives and false negatives.
Technical Considerations and Limitations
Because our initial dataset is small (only 300 human reviewed records are available for supervised classification), and many of the tags only show up in 10% of the records, we limit our initial analysis to a small set of metadata tags. Because these tags are human-generated and do not conform to a limited and controlled vocabulary, there is inconsistency in the training data as well. Some tags are redundant, showing up in clusters (legal and litigation, for instance, have a 95%+ overlap). Other times, two categories that might be better approached as a single category cause a split that may greatly reduce the effectiveness of an ML based classifier. Human ambiguity is often amplified when used to train ML models, and we see that effect at work here.
Precision-Recall Curves
Because there is a class imbalance between positive and negative categorization (including versus excluding a tag) and false positives are unlikely to be a serious problem (though, as discussed above, there may be some scenarios, such as sampling, where we would want to avoid them), we’ll take a look at precision-recall curves for a few of the more commonly occurring tags.
For quick reference, *Precision* refers to how often a positive classification was correct. For example, if our model predicted that a “Legal” tag should apply correctly 9 times and incorrectly 1 time, the Precision would be 90%. *Recall* refers to how often a positive classification was accurately detected. For example, if 10 records should have been classified as Legal, and our model detected 8 of them, our recall rate would be 80%. Ideally, we would like to strike some kind of balance between these two metrics, something we can achieve by raising or lowering the probability threshold for including a record in a tag. For example, if our model assigned a 30% chance that a particular record should be classified as “Legal”, we might or might not set that assignment based on whether we are trying to improve precision or recall.
For a more technical/mathematical discussion of Precision and Recall, please consult the scikit learn documentation at:
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/model_selection/plot_precision_recall.html
Workbook
The jupyter notebook implementing a Precision-Recall visualization for the “Legal” tag is
available at:
https://github.com/geoffswc/IDL-DSOS-2023/blob/main/Precision-Recall-Tag.ipynb
This workbook uses the scikit-plot module from scikit-learn to generate a precison-recall curve for a tag used in the classification model. Keep in mind that there isn’t much benefit to analyzing tags that show up in less than 10% of the records, and some tags may result in an error, as positive observations may be so rare (fewer than 1-2% of the records) that there is insufficient data to train or apply an ML model (a random test/train split may have *no* observations for a rare tag such a small dataset).
The visualizations generated by this workbook are available in the next section.
Visualization and Interpretation
This section displays the PR curve for “Legal”, a tag that shows up in approximately 10% of the training records. Keep in mind that common tags like “Tobacco”, which show up in 90% of the records, are auto-assigned based on the source of the collection, and do not represent the common use case. As a result, “Legal” will provide a better overview for a common tag that does not apply to most records, and performs relatively well in our predictive model.
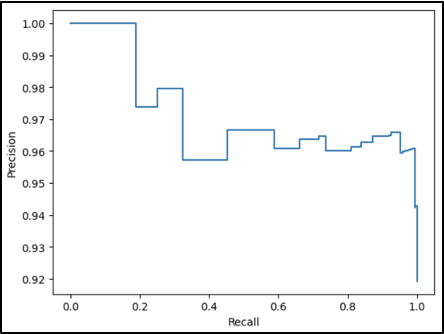
Precision-Recall
The precision recall curve for Legal indicates a wide threshold range that preserves usable precision and recall levels. Very high or low thresholds cause degradation of model performance, but precision and recall above 80% are available with flexibility to optimize for one or the other.
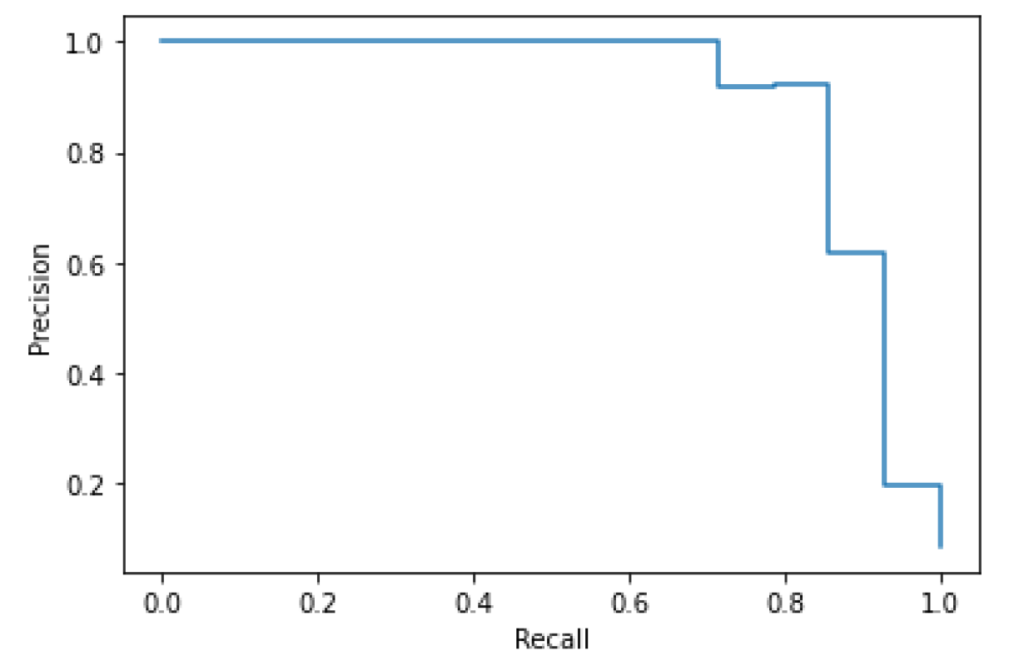
Precision/Recall-Threshold
This chart plots both precision and recall curves on the Y axis with the threshold level on the X axis. We see a rapid improvement of precision with a gradual, near-linear decrease in recall, indicating an effective threshold range well below 50%.
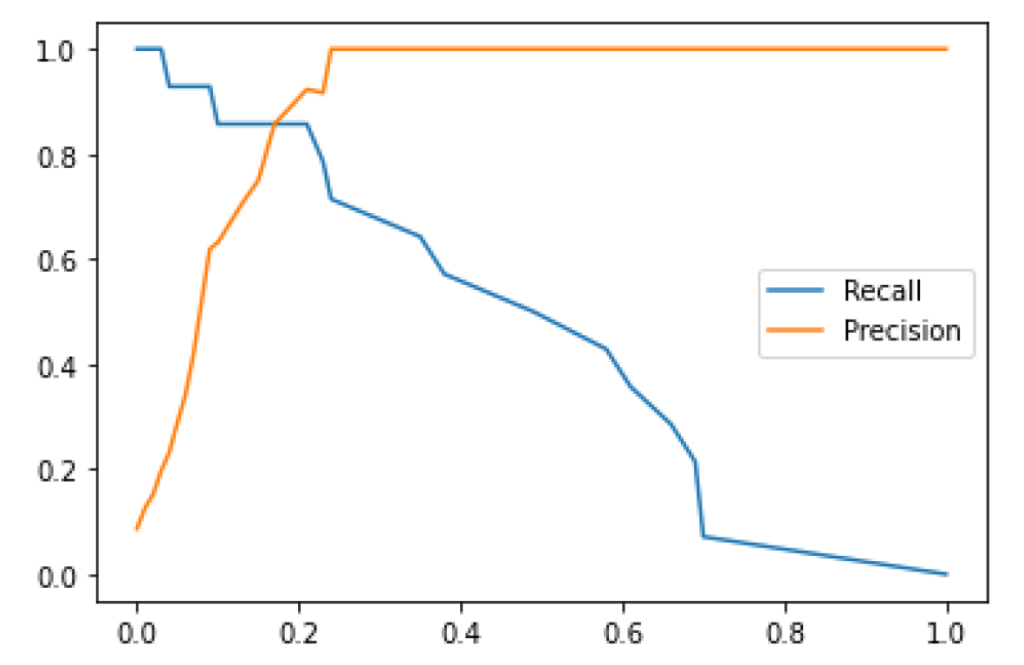
Production Application
Although our current data set is small, these results suggest that there is some value in using a supervised classification model to extend metadata to uncategorized documents based on ML generated transcript, though there are a number of challenges, and integrating these techniques into production would involve a number of decisions that are outside the scope of this pilot.
Challenges
A production rollout of an ML based model similar to this pilot would likely run into a number of issues with scale, such as:
- Training Data: our supervised machine learning model requires a set of categorized transcripts for training. This is a very time and labor intensive undertaking. We may not be able to create a sufficiently large and broad training dataset to create a meaningful model that covers even the most common tags.
- Varying Thresholds: The ideal threshold will vary based on the model performance for each individual tag and the research objectives. This variance, combined with the scale of processing required, may make customizable searches based on tag probability unrealistic in a production system.
- Availability of Transcripts: The tobacco, opioid, and other industry documents collections contain a large number of files (current estimate is 18 million), many are video or audio files without transcriptions. Without transcriptions available, it won’t be possible to apply the results of an ML model to make predictions for uncategorized documents.
Recommendations
This pilot does provide a template for an interesting and promising approach, and researchers may be interested in building their own ML models to analyze the transcripts in the collections.
We could provide some of this utility without a full production integration through the following:
- Pre-Built Transcription Datasets: The Industry Documents Library website currently provides pre-built transcription datasets for many image record collections. A similar initiative to provide transcriptions for video and audio would provide substantial benefit for researchers, independent of the ML based classification model.
- Classification Probability Estimates: Instead of integrating classification probabilities or tags into search, we could provide the ML output for each record in a pre-built dataset. This would leave the decision for setting a threshold up to researchers, but it would avoid the need to re-generate results based on model performance and researcher scenario for each tag. This approach might allow researchers to benefit from partial information.
- Generalized ML Models: Several AI tools, such as Google AutoML AI, do provide pre-trained models that can provide categorization. Because these models wouldn’t be trained specifically on our metadata, they may not capture the kind of classification most relevant to researchers, but they would eliminate the need for the very labor intensive generation of a training data set.