This is a guest post by Zach Bleemer. Zach is a Research Associate at UC Berkeley’s Center for Studies in Higher Education, where he directs the University of California Cliometric History Project, and a Graduate Intern in Institutional Research and Academic Planning at the UC Office of the President.
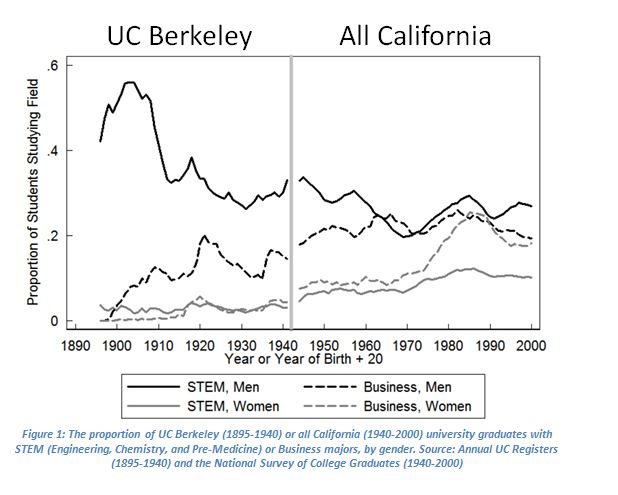
A few months ago, I gave a lecture entitled “A History of Higher Education in California: A Big Data Approach” at the UCSF Archives. The lecture presented a large trove of newly-collected UC student records from the first half of the 20th century, including a complete register of University of California undergraduate and graduate students—their names, home towns, degrees, and years of graduation—from 1893 to 1946. These records enable descriptive analysis like Figure 1, which extends well-documented trends in college major selection back to the late 19th century (for UC Berkeley).
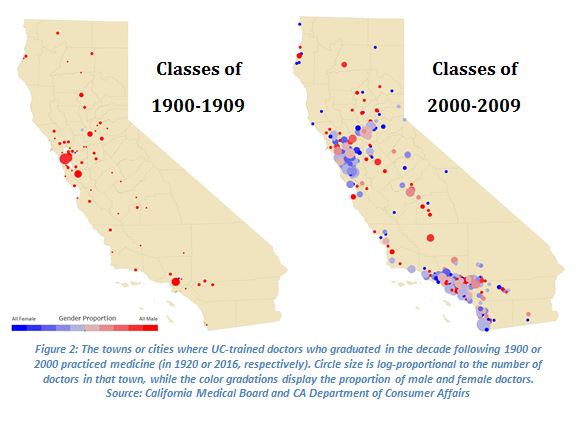
A recent Topic Brief published by the Institutional Research and Academic Planning Group (IRAP) at the UC Office of the President integrated this historical data with contemporary records of UC-trained medical professionals. Figure 2 uses California state medical license records from 1920 and 2016 to map the towns in which UC-trained doctors practice medicine, color-coding the towns by the doctors’ gender. Between 10 and 15 percent of UC medical students in the first decade of the 20th century were women, but women accounted for more than half of UC medical students in the first decade of the 21st century.
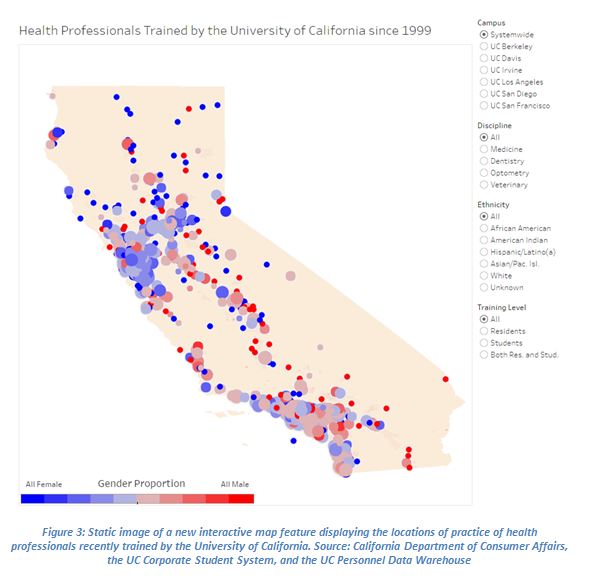
We also published an interactive map feature displaying the more than 850 cities and towns in which health professionals—doctors, dentists, optometrists, and veterinarians—trained by the University of California since 1999 currently practice, including both former graduate students as well as former residents (constructed by merging student and employment records with 2016 state licensing records). Toggles allow the viewer to restrict the map by UC campus, professional discipline, ethnicity, and level of training, and the map is color-coded by the professionals’ gender. The map displays both the demographic and geographic diversity of UC’s health-oriented graduates, who work in more than 60 percent of California towns with any health professionals. The interactive display also includes bar charts showing the number of health professionals who graduated UC each year (by campus and demographic group).
Both of these projects are part of a new initiative, A Century of Health, which aims to visualize and analyze the long-run contributions of UC’s health-oriented graduate schools to the state of California and beyond. Future components of this initiative will extend to pharmacists, nurses, physicians assistants, and more, and will leverage both new and very old sources of data, partly thanks to the UCSF Archives. The most exciting and comprehensive source of data is historical student transcripts housed in the UCSF Registrar, which we have recently concluded digitizing. A Century of Health aims to provide new insight into the University of California’s role in fostering wellness, economic mobility, and gender/ethnic equality across California by expanding, deepening, and repackaging information detailing the ubiquity of the University of California’s health-oriented graduate schools. To keep up with new developments, check the UC ClioMetric History Project’s website, or contact zachary.bleemer@ucop.edu.



 It is a privilege to offer this blog post as a follow-up and complement to my
It is a privilege to offer this blog post as a follow-up and complement to my 
